Understanding Diabetes: An Overview
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. There are two main types:
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease where the pancreas produces little to no insulin. This typically manifests in childhood or adolescence, requiring lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes: More common, often linked to lifestyle factors and obesity. The body becomes resistant to insulin, leading to increased blood sugar levels. Management strategies can vary from lifestyle modifications to medications, including insulin.
Key Strategies for Effective Diabetes Management
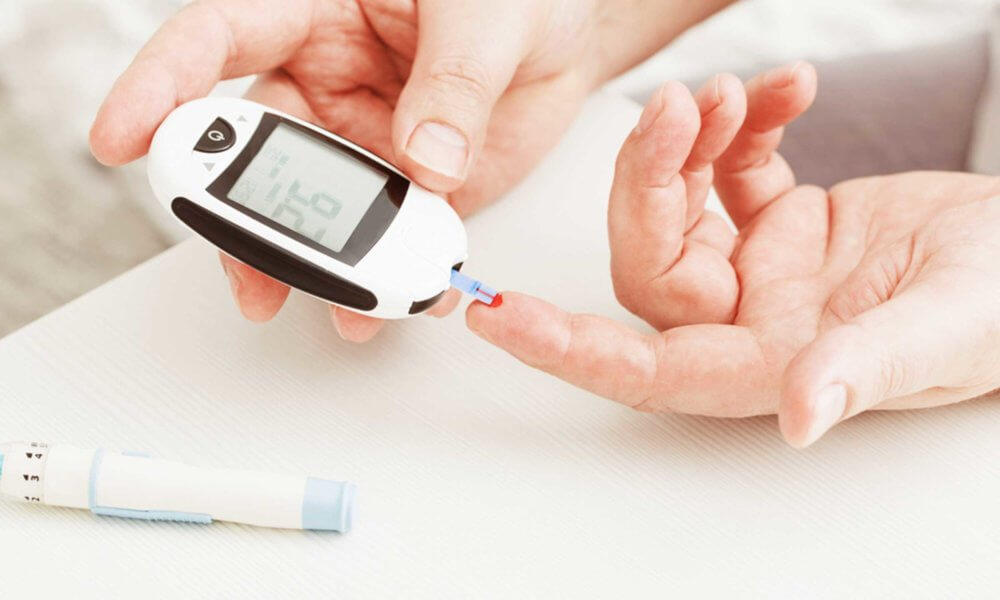
1. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
- Importance: Regular monitoring helps track how food, exercise, and medications affect your blood glucose levels.
- Methods: Use a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system.
- Targets: Work with your healthcare provider to determine your target blood glucose levels. Generally, fasting levels should be between 80-130 mg/dL, and post-meal levels should be under 180 mg/dL.
2. Nutrition and Meal Planning
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables.
- Carbohydrate Counting: Learn to count carbohydrates, as they directly affect blood sugar levels. Aim for consistent carbohydrate intake across meals.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil while minimizing saturated and trans fats.
- Portion Control: Use smaller plates, measure servings, and avoid second helpings to maintain portion control.
3. Regular Physical Activity
- Exercise Recommendations: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking or swimming, combined with strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Benefits: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, helps with weight management, and reduces the risk of heart disease.
4. Medication Management
- Types of Medications: Be aware of the different medications available for diabetes management, including:
- Insulin: Required for Type 1 diabetes and sometimes for Type 2.
- Oral Medications: Such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors, which help lower blood sugar levels.
- Adherence: Take medications as prescribed and communicate any side effects to your healthcare provider.
5. Education and Self-Management
- Diabetes Self-Management Education (DSME): Participate in DSME programs to learn about diabetes, meal planning, and blood sugar monitoring.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about diabetes through reputable resources, including books, websites, and local support groups.
6. Psychological Support
- Emotional Well-being: Diabetes can be overwhelming; consider working with a mental health professional if you're struggling with anxiety or depression.
- Support Groups: Join diabetes support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences can provide emotional relief and practical tips.
7. Regular Health Check-Ups
- Routine Monitoring: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare team, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators.
- Screening for Complications: Regular eye exams, foot exams, and blood tests to monitor kidney function and cholesterol levels are essential to catch complications early.
8. Stress Management
- Impact of Stress: Chronic stress can negatively affect blood sugar levels. Employ relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises.
- Mindfulness Practices: Mindfulness meditation can help improve emotional regulation and overall well-being.
9. Building a Support System
- Family and Friends: Communicate your needs and goals with loved ones, so they can support you in your journey.
- Healthcare Team: Establish a strong relationship with your healthcare team. Regular communication is vital for effective management.
10. Legal Rights and Advocacy
- Understanding Your Rights: Be aware of your rights regarding diabetes management in the workplace, including accommodations for medical appointments and necessary breaks for glucose monitoring.
- Advocacy Groups: Engage with diabetes advocacy organizations that work to protect and promote the rights of individuals with diabetes.
Conclusion
Diabetes management is a lifelong commitment that involves a holistic approach encompassing diet, exercise, medication, education, and emotional support. By implementing these comprehensive strategies, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition and enhance their quality of life. Always work closely with your healthcare team to tailor these strategies to your unique needs and circumstances. Remember, informed and proactive management can make a significant difference in living a healthy and fulfilling life with diabetes.

Hiç yorum yok: